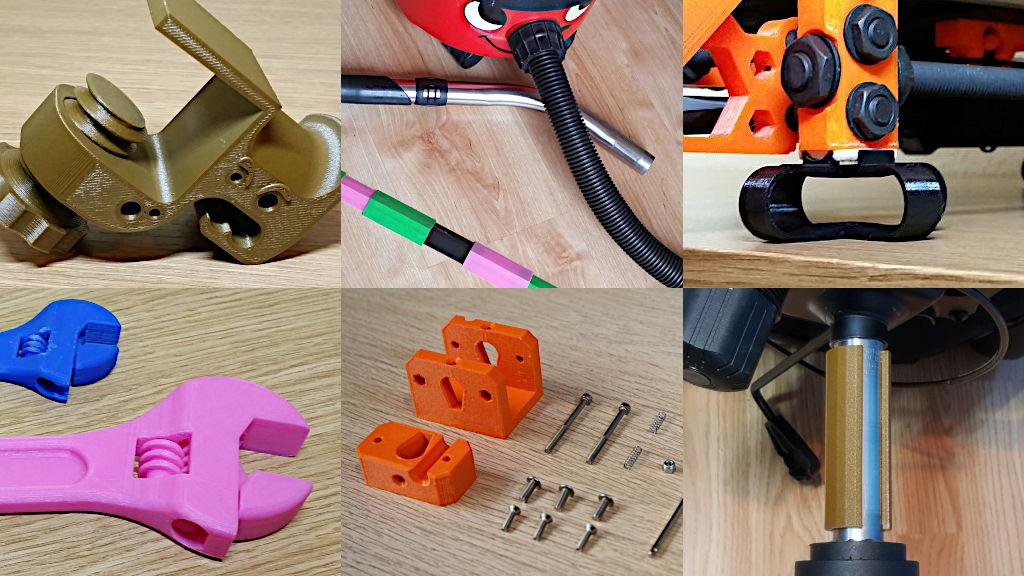
Best 3D Printable Objects: A Comprehensive Guide to Printing Success
In the realm of digital fabrication, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing the way we design, prototype, and manufacture objects. With its unparalleled capabilities and growing accessibility, 3D printing empowers us to create intricate designs, customize products, and explore new frontiers in innovation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of 3D printable objects, providing insights into the technology, its benefits, and the essential considerations for achieving successful prints.
From understanding the fundamentals of 3D printing to identifying the best printable objects, optimizing designs, and troubleshooting common issues, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to harness the full potential of this groundbreaking technology. Whether you’re a seasoned maker or just starting your 3D printing journey, this guide will be your indispensable companion.
Overview of 3D Printable Technology

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that allows the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital models. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which involve subtractive processes like cutting or molding, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, enabling the production of complex shapes and intricate designs.
The process begins with a digital model, created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is then sliced into thin layers, and the 3D printer builds the object by depositing material, such as plastic, metal, or ceramic, one layer at a time. This process continues until the object is complete.
3D printing offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing techniques. It allows for the rapid prototyping of new designs, reducing the time and cost of product development. It also enables the production of customized and personalized objects, as well as the creation of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using conventional methods.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are various types of 3D printing technologies available, each with its own strengths and limitations. Some of the most common include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is the most widely used 3D printing technology, which deposits molten plastic layer by layer to build the object.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin, building the object one layer at a time.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material, building the object layer by layer.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP uses a projector to cure liquid resin, building the object one layer at a time.
- Multi-Jet Modeling (MJM): MJM uses multiple jets to deposit droplets of liquid material, building the object one layer at a time.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing has found applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: 3D printing is used to create prototypes, custom parts, and end-use products.
- Healthcare: 3D printing is used to create medical devices, prosthetics, and tissue scaffolds.
- Construction: 3D printing is used to create building components, such as walls and roofs.
- Automotive: 3D printing is used to create car parts, such as dashboards and interior trim.
- Aerospace: 3D printing is used to create aircraft components, such as wings and engine parts.
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it is expected to find even more applications in the future, revolutionizing the way we design, manufacture, and use products.
Benefits and Considerations of 3D Printing

3D printing is a game-changer in manufacturing, bruv. It’s got sick advantages over traditional methods, like making stuff faster, cheaper, and more customized. But before you jump on the 3D printing hype train, let’s chat about the perks and potential drawbacks.
Cost-effectiveness
3D printing is the budget-friendly king. It cuts down on material waste and labor costs compared to traditional manufacturing. Plus, you can produce small batches or one-offs without breaking the bank.
Customization Options
Want to make a phone case that’s as unique as you? No problem with 3D printing. You can customize designs to your heart’s content, creating bespoke products that are a perfect fit for your needs.
Rapid Prototyping
3D printing is the Speedy Gonzales of prototyping. It lets you create physical prototypes in a flash, helping you test and refine designs quickly and easily.
Potential Drawbacks
Now, let’s talk about the potential downsides. 3D printing can be limited by the materials available and the size of objects you can make. Plus, it can take some time to perfect your printing skills.
Identifying the Best 3D Printable Objects

Choosing the right objects for 3D printing is crucial for successful prints. Consider these factors:
- File Format: Choose compatible file formats, such as STL or OBJ, which are widely supported by 3D printers.
- Complexity: Assess the complexity of the object. Simple designs are easier to print, while intricate ones may require advanced printers and expertise.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the object’s material is compatible with your printer. Different printers handle materials like PLA, ABS, and resin differently.
Optimizing 3D Models for Printing
To optimize 3D models for printing:
- Scale Appropriately: Ensure the model is scaled to fit your printer’s build volume.
- Repair Geometry: Use software to repair any holes or inconsistencies in the model’s geometry.
- Orient for Printing: Orient the model for optimal printing, considering factors like overhangs and supports.
- Add Supports: For models with complex geometries, add supports to prevent drooping or collapse during printing.
- Slice and Preview: Use slicing software to slice the model into layers and preview the print to identify any potential issues.
Materials and Techniques for 3D Printing
3D printing has expanded the horizons of design and manufacturing by enabling the creation of complex objects from a wide range of materials. The choice of material and printing technique significantly influences the quality, durability, and applications of 3D prints. Let’s delve into the different materials and techniques used in 3D printing.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
The most common materials used in 3D printing include:
- Plastics: PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon – Versatile and widely used for prototyping, toys, and household objects.
- Metals: Stainless steel, titanium, aluminum – Durable and strong, suitable for industrial applications and high-performance parts.
- Ceramics: Porcelain, stoneware, bone china – Intricate and heat-resistant, ideal for art, jewelry, and tableware.
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass – Lightweight and strong, used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
Techniques for 3D Printing
The three main techniques used in 3D printing are:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Melts and extrudes plastic filament, layer by layer, to create objects.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser to cure liquid resin, creating precise and smooth prints.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses a laser to fuse powdered material, resulting in durable and complex prints.
Impact of Material and Technique Selection
The selection of material and printing technique depends on the desired properties of the final product. For instance, FDM is suitable for quick prototyping, while SLA produces smoother prints with finer details. The choice of material affects the strength, durability, and flexibility of the object. By understanding the properties of different materials and techniques, you can optimize your 3D printing process for specific applications.
Design Considerations for 3D Printable Objects
Innit, blud? When it comes to 3D printing, your design game gotta be on point. You need to think about the strength of your objects, how flexible they gonna be, and how they gonna look. It’s like building a house, but with way more precision and no DIY disasters.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
CAD software is your secret weapon for creating 3D models that are gonna print like a dream. It’s like the blueprint for your objects, but instead of pen and paper, you’re using a computer. CAD software lets you create precise designs, tweak dimensions, and even simulate how your objects will behave when they’re printed. It’s like having a virtual workshop at your fingertips, innit?
Optimizing Designs for Printability
Now, let’s chat about making your designs print-ready. First off, you gotta consider the size of your object. If it’s too big, you might need to split it up into smaller parts. Next, think about the orientation of your object on the print bed. Different orientations can affect the strength and quality of your print.
Post-Processing
Once your object is printed, it might need a bit of TLC. You might need to remove support structures, sand it down to make it smooth, or even paint it to give it a bit of flair. Post-processing is like the finishing touches that make your 3D prints look and feel pro.
Troubleshooting Common 3D Printing Issues
Yo, printing with a 3D printer can be lit, but sometimes you might run into some snags. Don’t fret, mate! Let’s get to grips with some of the most common issues and how to fix them like a pro.
Warped Prints
When your prints come out all wonky and wavy, it’s probably because of warping. This happens when the bottom of the print cools too quickly, causing the top to contract and bend. To sort it out, try these tips:
– Use a heated print bed to keep the bottom warm and cozy.
– Lower the printing temperature to give the plastic more time to cool evenly.
– Add a brim or raft to the print to provide extra support.
Stringing
If you’re seeing thin strands of plastic connecting your prints, that’s called stringing. It happens when melted plastic seeps out of the nozzle when it’s not supposed to. To tackle this, try:
– Lower the printing temperature to reduce the flow of plastic.
– Increase the retraction distance to pull back the filament when the nozzle moves.
– Use a brim or raft to give the plastic something to stick to instead of your print.
Layer Separation
When the layers of your print aren’t sticking together properly, it’s known as layer separation. This can be a nightmare! To fix it, check out these solutions:
– Increase the printing temperature to make the plastic stickier.
– Slow down the printing speed to give the layers more time to bond.
– Use a glue stick or hairspray on the print bed to improve adhesion.
Importance of Maintenance and Calibration
Just like any machine, your 3D printer needs a bit of TLC to keep it running smoothly. Regular maintenance and calibration can prevent a whole host of issues. Make sure to:
– Clean the nozzle and print bed regularly.
– Calibrate the printer to ensure the nozzle is the right distance from the bed.
– Check the tension of the belts and pulleys to prevent skipping and layer shifting.
Post-Processing Techniques for 3D Prints

Polishing up your 3D prints is like giving them a swanky makeover. These techniques can turn your raw creations into masterpieces that’ll make your mates green with envy.
From sanding to painting and assembling, we’ll spill the beans on how to give your prints a pro finish.
Sanding
Sanding is the OG post-processing technique. Grab some sandpaper and get ready to smooth out those rough edges and layer lines. It’s like giving your prints a spa day, leaving them silky smooth and ready for the next step.
Smoothing
Smoothing takes sanding to the next level. Use acetone or chemical smoothers to melt away those pesky layer lines. It’s like giving your prints a facelift, leaving them with a flawless, glass-like finish.
Painting
Painting is the ultimate way to customize your prints and make them truly your own. From vibrant colors to metallic finishes, the possibilities are endless. Just make sure to prime your prints first, so the paint sticks like glue.
Assembling
If your prints have multiple parts, assembling them is the final step to bring your creation to life. Use glue or other adhesives to connect the pieces and watch your masterpiece take shape. It’s like building a LEGO set, but with your own unique designs.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in 3D Printing
3D printing technology is rapidly evolving, with new advancements and innovations emerging all the time. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what is possible with 3D printing, and opening up new possibilities for its use in a wide range of industries.
One of the most exciting trends in 3D printing is the development of new materials. These materials are stronger, more flexible, and more durable than traditional 3D printing materials, and they are opening up new possibilities for the use of 3D printing in demanding applications. For example, new metal alloys are being developed that can be used to 3D print parts for aerospace and automotive applications. These parts are lighter and stronger than traditional metal parts, and they can be produced more quickly and efficiently.
Another exciting trend in 3D printing is the development of new printing technologies. These technologies are faster, more accurate, and more versatile than traditional 3D printing technologies, and they are making it possible to 3D print objects that were previously impossible to produce. For example, new vat photopolymerization technologies are being developed that can print objects with extremely high resolution and detail. These technologies are being used to create realistic 3D models for use in movies, video games, and other applications.
The potential applications of 3D printing are vast. 3D printing is already being used in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and construction. In healthcare, 3D printing is being used to create custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides. In manufacturing, 3D printing is being used to create prototypes, tooling, and finished products. In construction, 3D printing is being used to create custom building components, such as walls, roofs, and even entire houses.
The future of 3D printing is bright. As new materials and printing technologies are developed, the possibilities for 3D printing will continue to grow. 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the way we design, manufacture, and build things.
Challenges and Prospects
Despite the rapid growth of 3D printing, there are still some challenges that need to be overcome. One challenge is the cost of 3D printers and materials. 3D printers can be expensive, and the materials used to print objects can also be costly. This can make it difficult for some people to access 3D printing technology.
Another challenge is the quality of 3D printed objects. 3D printed objects can sometimes be rough or have imperfections. This can make them unsuitable for some applications. However, as 3D printing technology continues to develop, the quality of 3D printed objects is improving.
Despite these challenges, the future of 3D printing is bright. As new materials and printing technologies are developed, the possibilities for 3D printing will continue to grow. 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the way we design, manufacture, and build things.
Q&A
What are the key advantages of 3D printing over traditional manufacturing methods?
3D printing offers several advantages, including cost-effectiveness for small-scale production, rapid prototyping capabilities, design customization, and the ability to create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
What factors should be considered when selecting objects for 3D printing?
When selecting objects for 3D printing, consider factors such as file format compatibility, complexity of the design, and the material properties required for the intended application.
What are the most common problems encountered in 3D printing and how can they be resolved?
Common 3D printing issues include warping, stringing, and layer separation. These issues can be resolved by adjusting printing parameters, optimizing the design for printability, and ensuring proper printer maintenance and calibration.
What post-processing techniques can be used to enhance the quality of 3D prints?
Post-processing techniques such as sanding, smoothing, painting, and assembling can significantly improve the aesthetics and durability of 3D prints.
What are the emerging trends and innovations in 3D printing technology?
3D printing technology is constantly evolving, with advancements in materials, printing techniques, and software. These innovations are expanding the applications of 3D printing into new industries and opening up new possibilities for innovation.