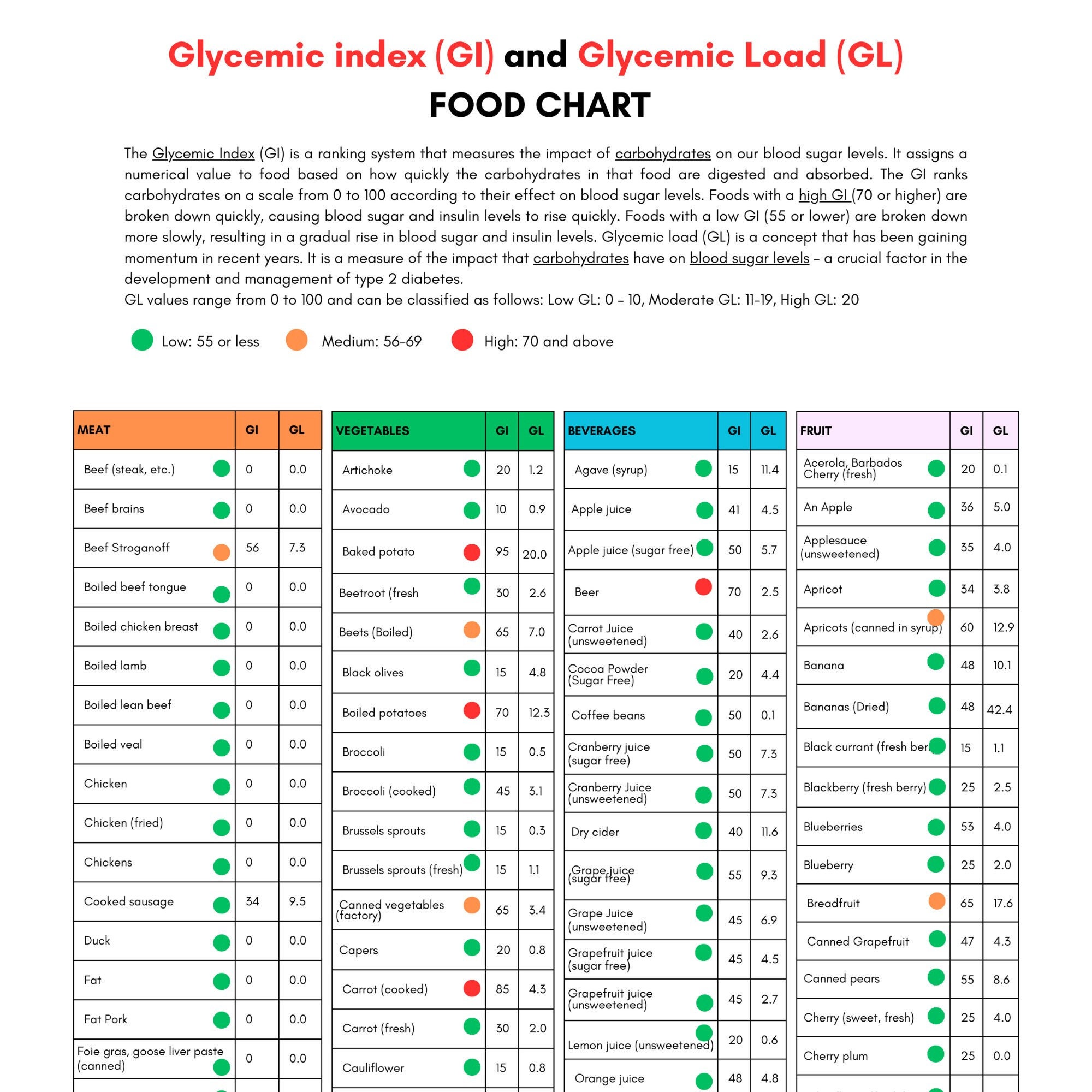
Glycemic Index Chart Printable: A Guide to Blood Sugar Management
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Understanding the concept of glycemic index (GI) is key to making informed food choices and effectively controlling blood sugar. A printable glycemic index chart can be a valuable tool in this journey, providing a comprehensive reference guide to navigate the world of carbohydrates and their impact on blood sugar.
The glycemic index measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood sugar levels. Low-GI foods release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing spikes and crashes in blood sugar. In contrast, high-GI foods cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, which can lead to insulin resistance and other health concerns. A printable GI chart empowers individuals to identify and choose foods that support their blood sugar management goals.
Definition of Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises your blood sugar levels. It’s a number between 0 and 100, with 0 being the slowest and 100 being the fastest.
Foods with a high GI are quickly broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, which can lead to weight gain, diabetes, and other health problems.
Foods with a low GI are more slowly broken down into glucose, which means they don’t cause as much of a spike in blood sugar levels. This can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risk of developing diabetes and other health problems.
Measuring GI
The GI of a food is measured by comparing it to the GI of pure glucose, which is 100. A food with a GI of 50 means that it raises blood sugar levels about half as quickly as pure glucose.
The GI of a food can be affected by a number of factors, including:
- The type of carbohydrate in the food
- The amount of fiber in the food
- The way the food is cooked
Importance of Glycemic Index

The Glycemic Index (GI) is a crucial factor in managing blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes. It measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood sugar levels after consumption.
Low-GI foods release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar. This is beneficial for several reasons:
Sustained Energy Levels
Low-GI foods provide a steady source of energy, preventing fluctuations in blood sugar levels that can lead to fatigue or energy crashes.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Regular consumption of low-GI foods has been linked to a reduced risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
Improved Weight Management
Low-GI foods promote satiety and fullness, reducing hunger and cravings, which can aid in weight management efforts.
Food Sources with Low, Medium, and High GI
Knowing the GI of foods can help you make healthier choices and manage your blood sugar levels. Here’s a table that categorizes foods based on their GI values:
Low GI (GI value 55 or less)
- Oats (GI: 55)
- Brown rice (GI: 50)
- Quinoa (GI: 53)
- Lentils (GI: 30)
- Sweet potatoes (GI: 46)
- Apples (GI: 36)
- Berries (GI: 25-53)
Medium GI (GI value 56-69)
- White bread (GI: 75)
- Whole-wheat bread (GI: 58)
- Basmati rice (GI: 58)
- Pasta (GI: 50-60)
- Potatoes (GI: 65)
- Bananas (GI: 51)
- Grapes (GI: 59)
High GI (GI value 70 or more)
- White rice (GI: 89)
- Cornflakes (GI: 85)
- Sugary drinks (GI: 75)
- White potatoes (GI: 111)
- Dates (GI: 103)
- Watermelon (GI: 72)
- Pineapple (GI: 66)
Benefits of Using a Glycemic Index Chart

A Glycemic Index (GI) chart is a handy tool that can help you make informed food choices. By knowing the GI of different foods, you can choose foods that will help you maintain a healthy blood sugar level. This can be especially beneficial for people with diabetes or prediabetes.
Having a printable GI chart on hand can be a great way to make sure you’re making healthy choices when you’re eating out or shopping for groceries. You can quickly and easily check the GI of different foods so you can make informed decisions about what to eat.
A GI chart can help you:
- Make healthier food choices
- Manage your blood sugar levels
- Reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes
- Lose weight
Considerations When Using a Glycemic Index Chart

Yo, bruv! Before you start using that GI chart like a pro, there are a few bits you need to bear in mind.
First off, the GI value of a food can change depending on how it’s cooked or how ripe it is. So, that juicy apple you’re munching on might have a different GI than the one you baked in your crumble.
Individual Dietary Needs
Not everyone’s the same, so it’s important to consider your own dietary needs when using a GI chart. What works for your mate might not be the best option for you.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you’re not sure how to use a GI chart or if you have any specific health concerns, it’s always a good idea to chat with a healthcare professional. They can help you tailor a diet that’s right for you.
FAQs
What factors can affect GI values?
GI values can be influenced by food preparation methods, ripeness, and processing techniques.
How often should I update my printable GI chart?
Regularly update your chart to reflect the latest scientific research and dietary recommendations.
Can I use a GI chart to manage other health conditions?
While the GI chart primarily focuses on blood sugar management, it can also provide insights for managing conditions like heart disease and weight loss.