3D Printable Skulls: Revolutionizing Medicine, Education, and Art
The advent of 3D printing technology has opened up a new frontier in the creation of realistic and highly detailed skulls. These 3D printable skulls are transforming various fields, including medicine, education, and art, by providing innovative solutions and unlocking creative possibilities.
From aiding in complex surgical procedures to serving as educational tools and inspiring artistic endeavors, 3D printable skulls are revolutionizing our understanding and interaction with this fascinating part of human anatomy.
Definition and Overview

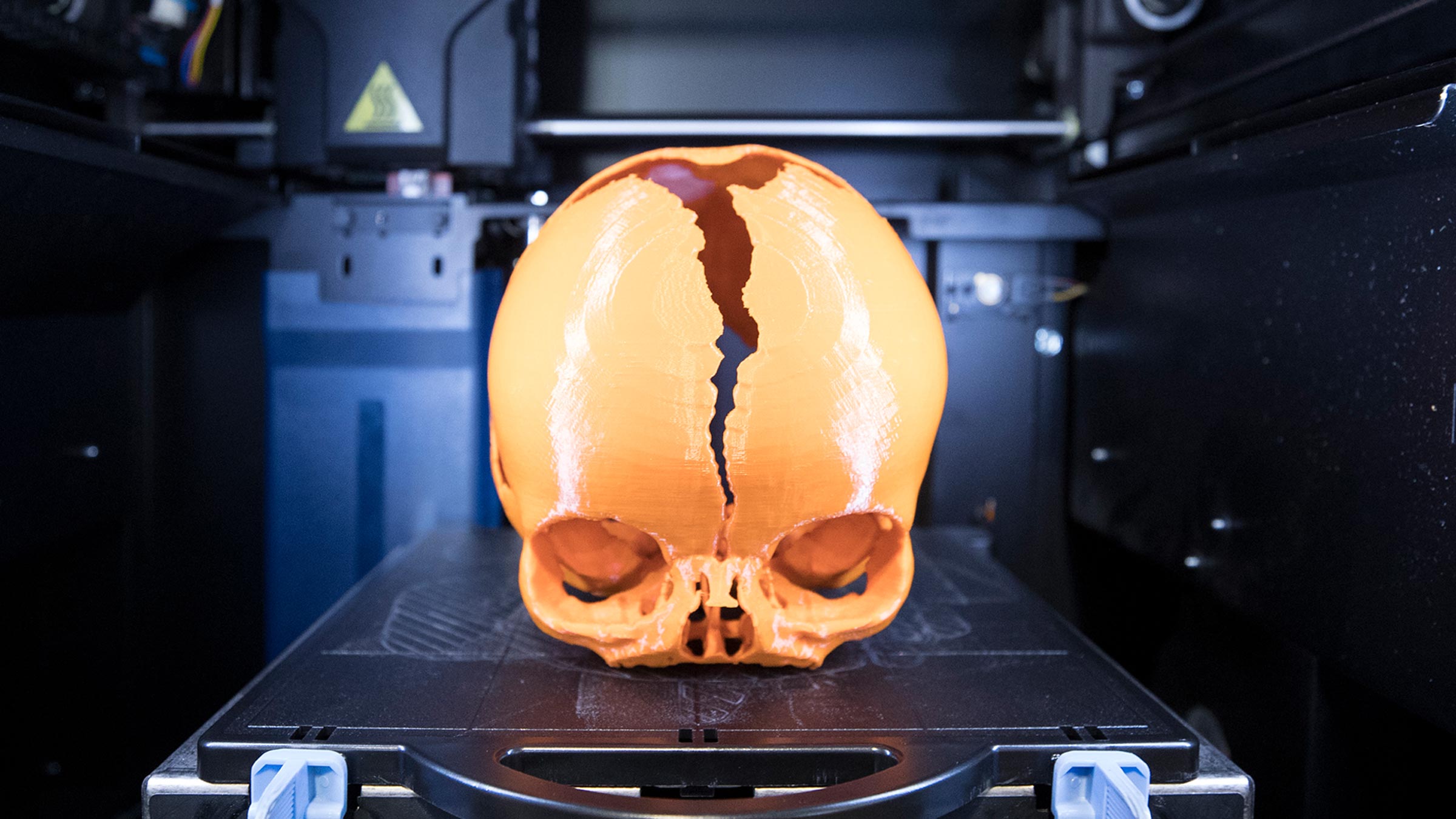
3D printable skulls are physical replications of human skulls created using 3D printing technology. These skulls are typically made from materials like plastic, ceramic, or metal and are designed to mimic the anatomical features of a real human skull. 3D printing allows for the precise and intricate creation of these skulls, enabling customization and personalization to meet specific needs.
The applications of 3D printed skulls are diverse, ranging from medical education and surgical planning to forensic investigations and historical research. In medicine, 3D printed skulls serve as valuable tools for studying human anatomy, practicing surgical procedures, and developing personalized implants. Forensic experts use these skulls to assist in facial reconstruction and identification of human remains. Additionally, 3D printed skulls have found applications in historical research, providing insights into ancient civilizations and human evolution.
Medical Applications

3D printed skulls have a range of medical applications, revolutionizing the field of healthcare.
They offer significant benefits for surgical planning and reconstruction, providing a precise and customized approach to patient care.
Surgical Planning
- 3D printed skulls serve as accurate anatomical models, enabling surgeons to plan complex procedures with greater precision.
- They allow for a thorough understanding of the skull’s structure and potential surgical challenges.
- This enhanced planning leads to improved surgical outcomes and reduced risks for patients.
Reconstruction
- 3D printed skulls are used to reconstruct damaged or deformed skulls, restoring their function and aesthetics.
- Custom-made implants can be designed to match the patient’s exact anatomy, ensuring a perfect fit.
- This technique offers hope to patients with severe skull injuries or congenital skull defects.
Personalized Medicine
- 3D printed skulls contribute to the advancement of personalized medicine by providing tailored solutions for each patient.
- The ability to create patient-specific models enables surgeons to plan and execute procedures that are unique to their individual needs.
- This approach enhances patient outcomes and improves overall healthcare delivery.
5. Design and Customization

Designing and customizing 3D printable skulls requires careful consideration of various factors to achieve the desired outcome.
Design Considerations
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Scale and Dimensions | Accurately measure the size and dimensions of the target skull to ensure a precise fit. |
| Geometry | Pay attention to the complex geometry of the skull, including its shape, contours, and surface details. |
| Wall Thickness | Determine the appropriate wall thickness to balance strength, weight, and printability. |
| Infill Density | Choose the optimal infill density to provide structural support and prevent deformation. |
| Support Structures | Consider the need for support structures to prevent overhangs and ensure stability during printing. |
Software and Resources
- Meshmixer: Comprehensive software for editing, repairing, and preparing 3D models for printing.
- Blender: Open-source 3D modeling software with advanced tools for sculpting and animation.
- ZBrush: Industry-standard software for detailed sculpting and creating intricate models.
- Free3D: Website offering a vast collection of free 3D models, including skulls.
- Thingiverse: Online community where users can share and download 3D models, including skulls.
Customization Options and Materials
3D printing technology allows for extensive customization of skulls. Options include:
- Size and Shape: Scale the skull to fit specific needs or create unique shapes.
- Surface Texture: Choose from a range of surface textures, such as smooth, rough, or textured, to enhance realism.
- Materials: Select from a variety of materials, such as PLA, ABS, or TPU, each with different properties and applications.
6. Future Advancements and Challenges

The realm of 3D printed skulls is ripe with prospects and hitches. Advancements in printing tech promise to revolutionize skull applications, but challenges persist.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
3D printed skulls pose unique ethical dilemmas. Concerns arise regarding patient consent, intellectual property rights, and the potential for misuse. Establishing clear regulations is crucial to ensure responsible use.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the materials used in 3D printing skulls?
Various materials can be used, including biocompatible materials like PLA, ABS, and PEEK for medical applications, and more durable materials like nylon and resin for educational and artistic purposes.
How are 3D printed skulls used in surgical planning?
3D printed skulls provide surgeons with accurate and detailed models of a patient’s skull, allowing for precise preoperative planning and improved surgical outcomes.
What are the advantages of using 3D printed skulls in education?
3D printed skulls offer students a tangible and interactive way to study human anatomy, enabling them to visualize and manipulate skull structures in a more immersive manner.
How are 3D printed skulls used in art and design?
Artists and designers use 3D printed skulls as unique and customizable canvases for their creations, creating intricate and visually striking pieces that explore various themes and concepts.